Cannabidiol (CBD) is a cannabis derived chemical compound called phytocannabinoid that act on the cannabinoid receptors in our brains. Currently, there are 113 identified cannabinoids, THC (tetrahydrocannabinol) being a popular one.
Unlike THC, CBD is non-intoxicating- that means that it won’t make a person feel high. It doesn’t affect cognition and has anti-inflammatory action. It has been seen to reduce anxiety in patients. It also has a positive effect on the skin and removes germs due to its anti-inflammation properties antimicrobial properties.
It is often sold as CBD oil which has cannabidiol as the single active component. It may also be available as CBD dominant hemp extract oil or a prescription liquid. It is also available as a spray that may be applied to the skin.
Cannabidiol has been used to treat epilepsy in the United States.
How does it work?
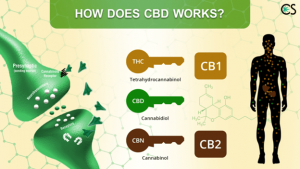
Cannabidiol is a cannabinoid, and they work by interacting with certain receptors in the body. Two types of receptors have been identified in the human body called CB1 and CB2 cannabinoid receptors.
CB1 receptors are spread all over the human body and many are also present in the brain. Compared to CB1, CB2 receptors are relatively confined to the immune system.
The effects of these two receptors are also different. The CB1 receptors in the brain may affect mood, motion, thought process, appetite. THC is known to attach with these receptors. Comparatively, CB2 receptors tend to have an effect on inflammation and pain.
CBD was thought to attach to the CB2 receptor, but new research has now shown that it is not the case. Scientists still haven’t been able to figure out the exact mechanism of action of CBD.
Image Credit: www.cbdschool.com
CBD has been seen to instead modulate different receptors and ion channels of the human body. Some receptors that CBD has been seen to modulate are-
Inhibits serotonin receptors:
CBD has been seen to activate the 5-HT1A (hydroxytryptamine) serotonin receptor, hence inducing an anti-anxiety effect. Its is supposed to be anti-emetic and has anti nausea properties.
Anti-inflammatory & therapeutic effect:
CBD interacts with numerous ion channels for a therapeutic effect. It binds to TRPV1 receptors, which are known to work as ion channels. TRPV1 has the ability to mediate pain perception, inflammation and body temperature.
Acts as antagonist:
Studies indicate that CBD has a tendency to act as an antagonist that blocks, or deactivates, another G protein-coupled receptor called GPR55. By blocking GPR55 signaling, CBD may have an effect on our body which helps decrease both bone re-absorption and cancer cell proliferation.
| [icon type=”icon-lamp”] 50% Off Diamond CBD Use promo code DIAMOND50 and get 50% off on all Diamond CBD products for one time usage |
|---|
Anti cancer:
CBD also shows an anti-cancer effect due to activation of PPARs [Peroxisome Proliferators Activated Receptors] that are located on the surface of the cell’s nucleus.
Alzheimer’s:
PPAR-gamma activation degrades amyloid-beta plaque, a key molecule associated with the development of Alzheimer’s disease. Hence, cannabidiol which is a PPAR-gamma agonist, may be a useful cure for Alzheimer’s patients.
GABA-A Receptor:
CBD reduces anxiety by changing the shape of the GABA-A receptor in a way that amplifies the natural calming effect of GABA.
- Nurturing Your Child’s Growth – The Daycare Advantage - October 19, 2024
- Things to Do in the Big Apple: A Comprehensive Guide to New York City - September 30, 2024
- Building a Team: Creating Unforgettable Family Moments on a Budget - September 24, 2024
- Top 10 Tips for Good-Quality Sleep For A Relaxed Mind - September 18, 2024
- Unveil Face Massage Benefits For Brighter & Glowing Skin - April 9, 2024
- Menstrual Hygiene 101: Essential Tips for a Healthy Period - April 9, 2024
- Best Home Remedies for Pain During Periods - April 9, 2024
- 10 Postnatal Exercises That You Should Try After Pregnancy - April 9, 2024
- Prepare with Ease: Maternity Hospital Bag Checklist - April 9, 2024
- Understanding the Stages of Labour – What To Expect During Delivery? - April 9, 2024